Key Summary
• The U.S. economy is expanding, supported by steady consumer spending despite uneven manufacturing and tariff pressure.
• Core global manufacturing is stabilizing, with strength in India and Southeast Asia contrasted by weakness in Europe and mixed results in China.
• North American PCB shipments rose sharply while EMS shipments declined, though bookings indicate resilient demand.
• Rising material and labor costs continue to squeeze margins across the electronics supply chain.
• Tariff uncertainty remains a central risk shaping investment, pricing, and future production trends.
Welcome to Industry Intelligence Insights, your monthly guide to the trends and data shaping the global electronics manufacturing landscape. I’m Thiago Guimarães, Director of Industry Intelligence at the Global Electronics Association, and I’m pleased to share the latest updates.
This month’s issue arrives as the U.S. economy continues to expand, supported by resilient consumers and steady hiring, even as manufacturing faces uneven momentum and tariff pressures. Our Chief Economist examines these dynamics, highlighting both the drivers of growth and the risks that could weigh on the outlook.
We also spotlight fresh data on the North American PCB and EMS markets, with shipments diverging but book-to-bill ratios pointing to resilient demand. July’s Global Sentiment Report underscores how rising material and labor costs continue to squeeze margins despite strong order books, while our latest blog explores how new tariffs on copper, semiconductors, and other goods are reshaping global supply chains.
Read on for timely intelligence to help you navigate what’s ahead.
Thiago Guimarães
Director of Industry Intelligence, Global Electronics Association
Market Analysis from Global Electronics Chief Economist Shawn DuBravac
The U.S. economy continues to expand, underpinned by resilient consumer spending and steady hiring, even as manufacturing remains uneven and tariff uncertainty pressures margins. There continue to be risks to the outlook, including a sharper slowdown driven by rising tariff and input costs, deteriorating credit conditions that curtail investment, and a softer labor market cooling consumer demand.
The U.S. economy grew at a 3.3% annualized pace in the second quarter, an upward revision from the 3% advance estimate and a clear rebound from the −0.5% contraction in Q1. The gain was led by a drop in imports, which mathematically boosts GDP, and firmer consumer spending, partly offset by weaker investment and exports. A useful gauge of underlying private demand, real final sales to private domestic purchasers, rose 1.9%. This pace points to steady domestic momentum even as headline GDP benefited from lower imports.
Inflation has firmed but remains moderate by recent standards. In July, headline CPI rose 2.7% year over year and core CPI increased 3.1%, with shelter still a key driver and energy prices lower than a year ago. The Fed’s preferred gauge told a similar story, with the PCE price index up 2.6% and core PCE up 2.9% from a year earlier. Month over month, both CPI and PCE advanced modestly, which points to steady but not accelerating price pressure, most visible in services while goods remain comparatively subdued.
Manufacturing continues to face headwinds. July’s durable goods report looked weak on the surface, new orders fell 2.8% after a 9.4% drop in June, but the decline was concentrated in transportation equipment, which fell 9.7%. The swing was driven by commercial aircraft, where orders are normalizing after the outsized Boeing purchase tied to President Trump’s Middle East tour. Excluding transportation, orders rose 1.1%, suggesting underlying goods demand is stabilizing. However, excluding defense, orders fell 2.5%, confirming volatile categories are skewing the headline.
Regional signals are mixed but a touch firmer than early summer. Chicago’s PMI slipped back to 41.5 in August and remains in contraction for the twenty-first straight month. New orders pulled back, employment fell to its lowest since June 2020, production softened, and backlogs declined, partly offset by longer supplier delivery times. A special question on tariffs found most firms expect clarity on input costs within three to six months, with the rest split among sooner, later, or unknown.
Conditions in the Richmond Fed district improved from July’s trough. The composite index rose to minus 7 from minus 20, with shipments, new orders, and employment all less negative. Vendor lead times lengthened, backlogs continued to shrink but at a slower pace, input price growth picked up, and selling prices were little changed. Firms’ six-month expectations were mixed, with better readings for future shipments and hiring, weaker local business conditions, and continued caution on equipment, software, and capital spending.
The Kansas City district was mostly flat but steadier. The month-over-month composite held at 1, up from minus 2 in June. Production and the workweek edged higher, the employment index moved to a neutral reading on a monthly basis, and most year-over-year gauges remained negative but improved, with employment still down on that longer look. Backlogs, export orders, and inventories stayed in contraction, while the future composite rose from 8 to 11 as firms anticipated better production and orders. Durable goods activity was mostly flat, nondurables slipped slightly, shipments and new orders increased modestly, and raw materials price pressure eased a bit even as finished goods prices ticked up. Nearly half of firms reported lower customer purchase volumes versus last quarter, and looking ahead to the rest of 2025 almost half expect stronger demand.
Texas stands out as a clear pocket of expansion. The production index remained elevated at 15.3, new orders turned positive for the first time since January at 5.8, shipments jumped to a three year high, and both employment and hours worked increased. Overall business activity hovered near zero, company outlooks improved slightly, and uncertainty rose. Price and wage pressures firmed, with raw materials inflation well above average and modest pass through to finished goods. Forward-looking indexes strengthened, including a double-digit gain in the future production index and a higher future general business activity reading.
Tariffs are a visible headwind. In Texas, more than 70% of manufacturers reported negative effects this year. Nearly half saw higher input costs, 27% raised selling prices, and almost 40% reported margin compression. Among firms that passed cost increases to customers, most did so only partially, and only about one quarter achieved full pass through.
Taken together, U.S. manufacturing appears to be forming a floor rather than sliding into a broad downturn. The aircraft swing distorted July’s headline orders while core orders edged higher. The Midwest remains soft, the Mid Atlantic is less negative, the Plains are flat with improving visibility, and the Southwest is expanding. Backlogs are thinning in several districts, lead times are lengthening, and price pressures are most visible upstream. Hiring is selective where demand supports it, capital spending plans remain cautious, and tariff related cost uncertainty is squeezing margins. Over the next few months, we will be closely watching core orders, tariff pass through and margins, and any turn in capex intentions that would mark a shift in expectations.
In the Eurozone, growth remains modest. In the second quarter, euro area GDP increased 0.1% quarter over quarter and 1.4% year over year, while the broader EU rose 0.2% on the quarter. The country pattern is still divergent, with Spain up 0.7% quarter-over-quarter and France up 0.3%, set against slight declines in Germany and Italy at −0.1% each.
Inflation is hovering a touch above the European Central Bank’s target. The August flash estimate put euro area HICP at 2.1% year over year, with “core” inflation, excluding energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco, at 2.3%.
The European manufacturing sector showed the first clear signs of a turn, although hard data are still uneven. The HCOB/S&P Global Eurozone Manufacturing PMI rose to 50.7 in August, the first expansion since early 2022, with factory output growth at a 41-month high. The euro area Composite PMI edged up to 51 in August, signaling only modest overall growth. In hard data, industrial production fell 1.3% month over month in June but was up 0.2% year over year.
In China, the economy is growing near the government’s “around 5%” target, but momentum is uneven. Headline GDP rose 5.2% year over year in the second quarter, and 5.3% for the first half but the mix still looks fragile given weak domestic demand, property drag, and tariff uncertainty that could weigh on second half growth. China’s factory picture remains mixed. The official NBS manufacturing PMI edged up to 49.4 in August from 49.3 in July, which means activity is still contracting, while the privately compiled RatingDog China General Manufacturing PMI, produced with S&P Global, surprised to the upside at 50.5, the best in five months. The private survey showed stronger overall new orders, a renewed build-up of backlogs, rising input costs, and continued job shedding, while export orders remained weak. Hard data are consistent with margin pressure upstream, with July industrial output up 5.7% year over year and producer prices down 3.6% year over year. Taken together, surveys point to a tentative stabilization led by domestic orders and some services spillover, while deflation at the factory gate and soft external demand keep the recovery fragile.
In Japan, the Jibun Bank manufacturing PMI came in at 49.7 in August, still below 50 as export orders fell sharply. Japan’s July industrial production declined 1.6% month over month, with shipments lower and inventories higher, and the official outlook points to a rebound in August followed by a dip in September. South Korea’s manufacturing PMI was 48.3 in August, and customs data showed exports up just 1.3% year over year as new U.S. tariffs weighed on U.S.-bound shipments, even as semiconductor exports surged 27.1% and the trade surplus held.
Taiwan shows the same bifurcation. The manufacturing PMI remained in contraction at 47.4 in August, yet July hard data were strong, with export orders at $57.6B, up 15.2% year over year, and manufacturing output up 19.6% year over year, reflecting AI and high-performance computing demand feeding through the tech sector. The mix suggests firms remain cautious as they gauge tariff and demand risks, while realized production and order books continue to benefit from the chip upcycle.
South and Southeast Asia remain the relative bright spot, led by India. India’s manufacturing PMI jumped to 59.3 in August, the fastest pace in more than 17 years, driven by strong domestic demand, ongoing hiring, and higher input and output prices that firms largely passed through. Across ASEAN, the regional PMI report shows conditions improving from July’s trough, with Thailand expanding the fastest among the big five, Indonesia returning to growth, Vietnam still modestly above 50, the Philippines sustaining expansion, and Malaysia near-stabilized at 49.9.
Overall, global manufacturing shows signs of stabilization in select regions, but the environment remains fragile and uneven, with tariffs, margin pressure, and domestic demand dynamics shaping the outlook for the months ahead.
Book to Bill
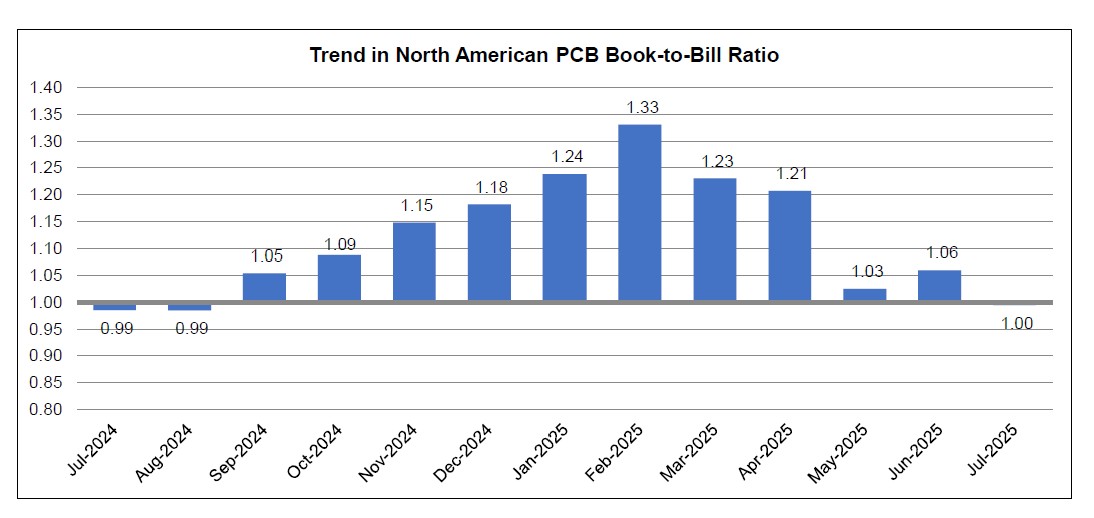
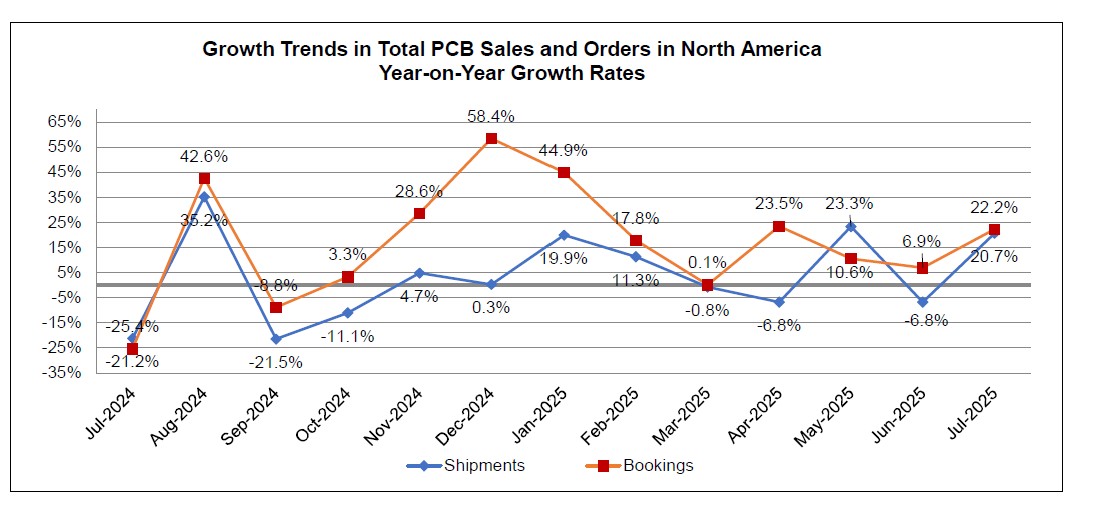
PCB: North American PCB Industry Shipments Up 20.7 Percent in July
North American PCB shipments surged 20.7% in July 2025 from last year, with bookings up 22.2% year-over-year. The book-to-bill ratio held steady at 1.00, signaling that output is keeping pace with demand as industry activity strengthens.
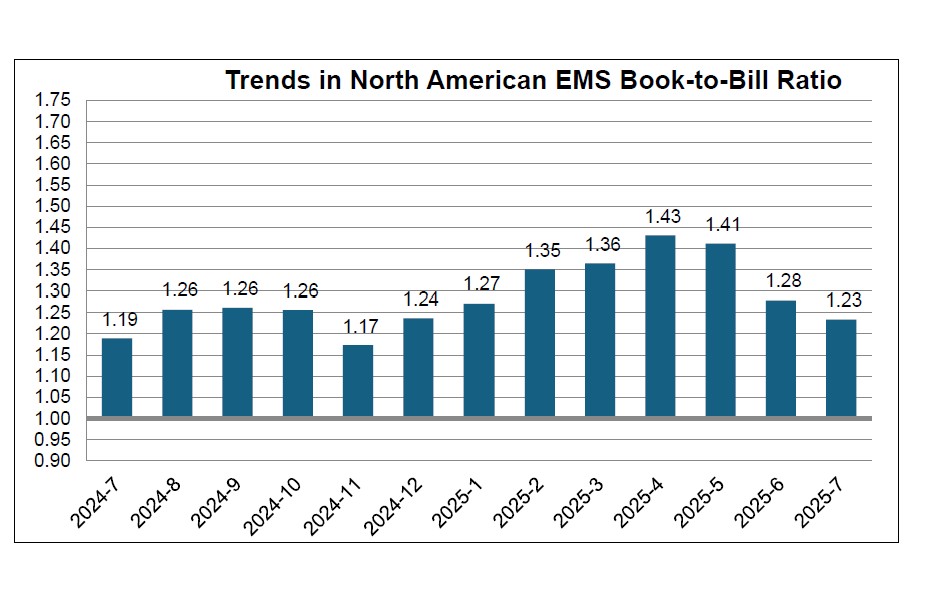
EMS: North American EMS Industry Shipments Down 4.1 Percent in July
North American EMS shipments declined 4.1% in July 2025 compared to last year, though bookings rose 7.9% year-over-year. With a book-to-bill ratio of 1.23, demand continues to outpace supply, pointing to strengthening orders despite softer shipment activity.
Global Sentiment
The Current Sentiment of the Global Electronics Manufacturing Supply Chain
July 2025 Global Sentiment: Despite persistent pressure from rising input costs, the outlook for shipments, orders, and capacity utilization improved over the month, indicating that while current conditions remain challenging, future industry expectations strengthened
Recent Reports
Market Intelligence Capabilities
The August 2025 Global EMS Sentiment Report shows manufacturers facing persistent margin pressures, with rising material and labor costs continuing to challenge profitability. Despite these headwinds, order books and utilization rates remain strong, signaling cautious optimism across the EMS supply chain.
Blogs/Other Write Ups
Global Perspectives: How New Tariffs Are Shaping the Electronics Industry
The Global Electronics Association welcomed the Trump Administration’s National AI Action Plan, calling for renewed investment in domestic electronics manufacturing as a critical foundation for AI leadership.
Upcoming Events:
-
- September 4, 2025—Evertiq Expo, Gothenburg, Sweden: Global Electronics Association’s Christoph Solka will present on the European EMS market.
- September 11, 2025 — TEK Day Gdansk, Poland: Global Electronics Association’s Christoph Solka will be giving a presentation on the European EMS market.
- September 17-18, 2025 — IPC Day (EMS) Paris, France
- September 24, 2025 – Elektronicaproductie: Made in Europe: De Toekomst van Elektronicaproductie, Leusden, Netherlands: Christoph Solka, Global Electronics Association, will offer insights into how the European EMS sector is responding to disruption and what lies ahead.