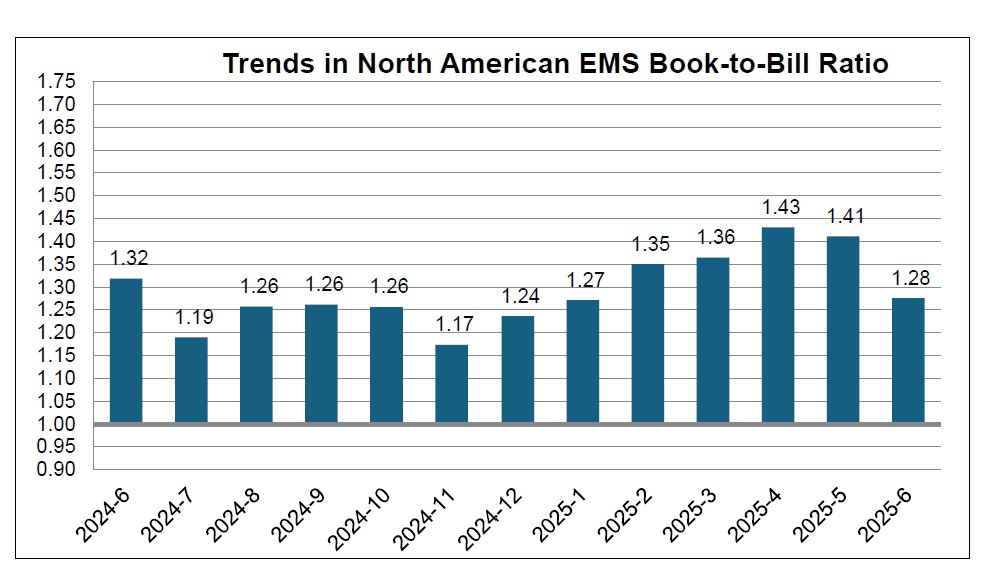
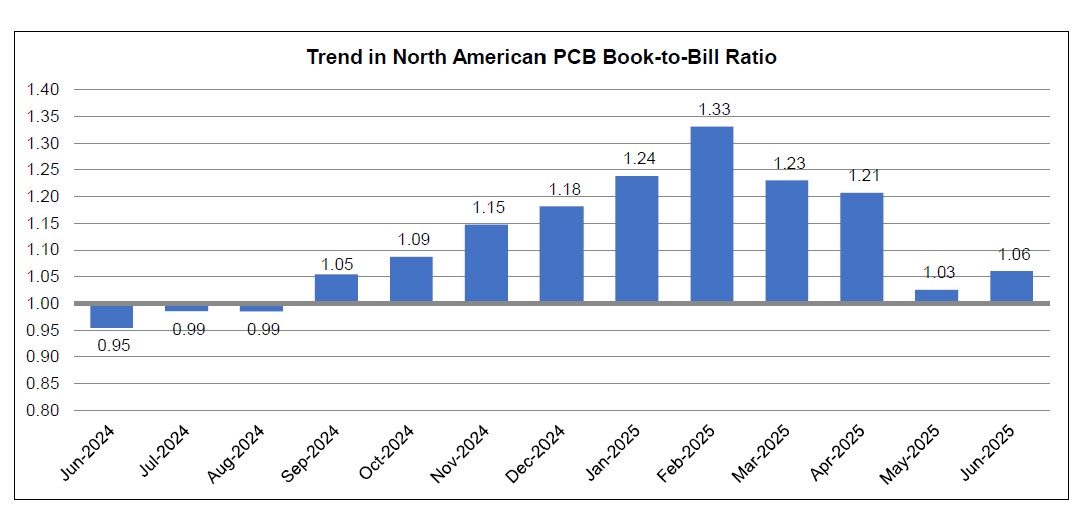
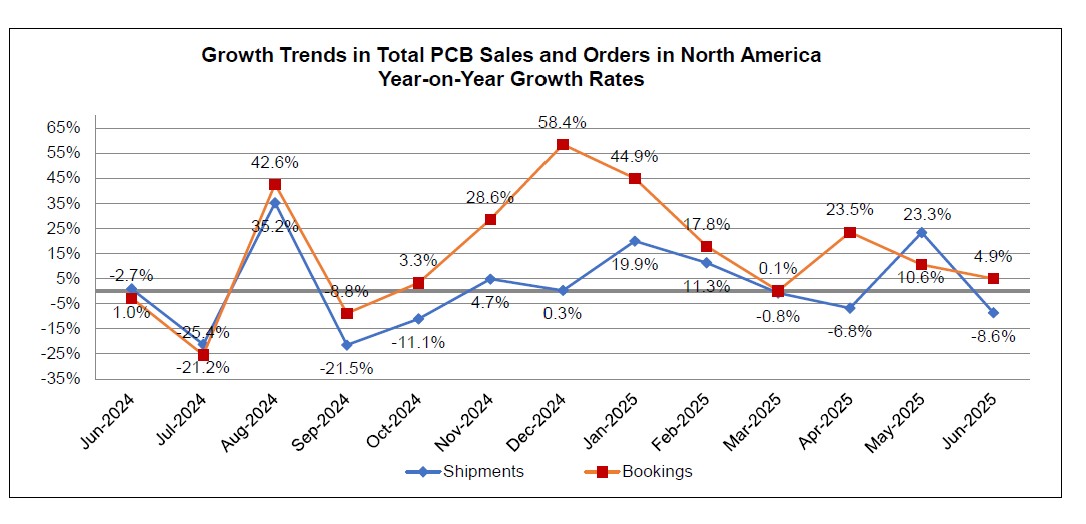
EMC Taiwan Receives IPC-4101 Qualified Products Listing Certification
IPC’s Validation Services Program has awarded an IPC-4101 Qualified Products Listing (QPL) to Elite Materials Co. (EMC), an electronics base material manufacturing company headquartered in Taoyuan City, Taiwan.
EMC produces copper-clad laminates, prepregs, and packaging substrates to the global electronics industry. EMC successfully qualified their product EM-371(Z) to specification sheet 126 of IPC-4101E WAM1, Specification for Base Materials for Rigid and Multilayer Printed Boards at an independent test lab according to Table 3-1. EMC also completed an intensive two-day audit where their manufacturing practices, test methods, certification and IPC-4101 conformance requirements were reviewed.
EMC met or exceeded IPC’s Validation Services QPL requirements for producing base materials used by printed circuit board manufacturers in the electronics industry. The company is now listed as an IPC-4101 trusted source capable of manufacturing in accordance with industry best practices for specification sheets 126. EMC and other trusted sources of suppliers can be found on IPC's QML/QPL (Qualified Product Listing) database.
About IPC's Validation Services Program
IPC’s Validations Services QPL/QML Program was developed to promote supply chain verification. It also provides auditing and certification of electronics companies' products and identifies processes which conform to a number of industry standards.
"EMC has differentiated itself in the high reliability FR-4 market by becoming part of IPC's global network of trusted industry sources. This is especially valuable as many defense and aerospace OEMs recognize the importance of Validation Services QPL for their supply chain." said David Bergman, Global Electronics Association vice president, international relations.
On behalf of EMC, Chairman Albert Tung commented, “Becoming a trusted source of copper-clad laminates and prepregs through the IPC Validation Services QPL/QML Program reinforces EMC’s commitment to the global military/aerospace markets. We are pleased to have one of our newest products, EM-371(Z), validated to IPC-4101E WAM 1 specification sheet 126 and look forward to adding additional products to the QPL in the near future.”